The Lactose Intolerance of Bacteria
 François Jacob and Jacques Monod sought to understand how bacteria made decisions to switch between sugars as sources of energy. Glucose is the preferred energy source of cells. Jacob and Monod found that if glucose and lactose were presented as food for bacteria, the glucose would first be utilized and the lactose would be digested after the depletion of glucose. This occurred because the bacteria would not produce the enzyme β-galactosidase which is responsible for digesting lactose to the monomers galactose and glucose. Monod found that when lactose was the sole sugar, the expression of the enzyme β-galactosidase was induced.
François Jacob and Jacques Monod sought to understand how bacteria made decisions to switch between sugars as sources of energy. Glucose is the preferred energy source of cells. Jacob and Monod found that if glucose and lactose were presented as food for bacteria, the glucose would first be utilized and the lactose would be digested after the depletion of glucose. This occurred because the bacteria would not produce the enzyme β-galactosidase which is responsible for digesting lactose to the monomers galactose and glucose. Monod found that when lactose was the sole sugar, the expression of the enzyme β-galactosidase was induced.
The Lac Operon
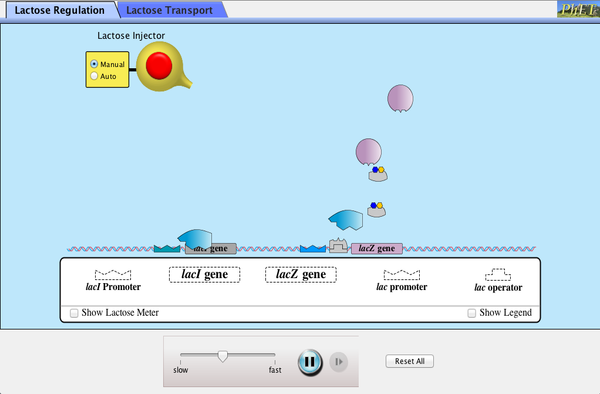
Jacob and Monod later found that the genes involved in utilizing lactose were clustered together in proximity under a coordinated control mechanism. This became known as the Lac operon.

The usage of lactose as a source of energy is preferred by bacteria when glucose is not present. In the presence of abundant glucose, it would be a waste of energy and cellular resources to commit to synthesizing the mRNA and the protein for β-galactosidase. Unless lactose is present, a protein binds to a portion of the Lac promoter referred to as the operator. This repressor protein is encoded by another gene (LacI) outside of the gene cluster. Occasionally, the repressor unbinds to the operator and RNA Polymerase is permitted to transcribe the LacZ gene (β-galactosidase), LacY gene (permease), and LacA gene (acetylase).This “leakiness” of expression is important since the permease protein is needed on the surface of the cell to allow lactose into the cell if it is present in the environment. The presence of lactose causes the repressor to fall off the operator to grant RNA pol access to the DNA. When glucose is low, a protein called CAP (Catabolite Activated Protein), binds to the Lac promoter and works as an recruitor of RNA pol. The coordinated effects of CAP activation and Lac Repressor inactivation yields high transcription of the operon.

Lac Operon Simulation
Launch the simulation below to explore the coordinated activation of the Lac Operon.